The GSM network, or Global System for Mobile Communications, has revolutionized the way we connect with one another across the globe. This digital mobile network standard is not just a technological marvel; it has transformed communication into an essential part of our everyday lives. By facilitating voice calls, SMS, and mobile data services, the GSM network has become synonymous with mobile connectivity. Understanding its structure and functionality is crucial for anyone interested in telecommunications or who simply wants to know how their mobile devices operate.
One of the most significant aspects of the GSM network is its widespread adoption. Almost all mobile devices today are built to operate on GSM technology, making it a universal standard. This has allowed users to roam seamlessly from one region to another without losing connectivity. The GSM network's ability to provide international coverage has made it indispensable for both personal and business communications in an increasingly connected world.
Moreover, the GSM network allows for a plethora of services beyond simple voice calls. With the advent of 2G, 3G, and now 4G LTE, GSM technology has evolved considerably. Each iteration has brought improvements in speed, reliability, and the range of services available. Understanding these advancements empowers users to take full advantage of their mobile devices, ensuring they can communicate effectively, whether for work or leisure.
What is the Structure of a GSM Network?
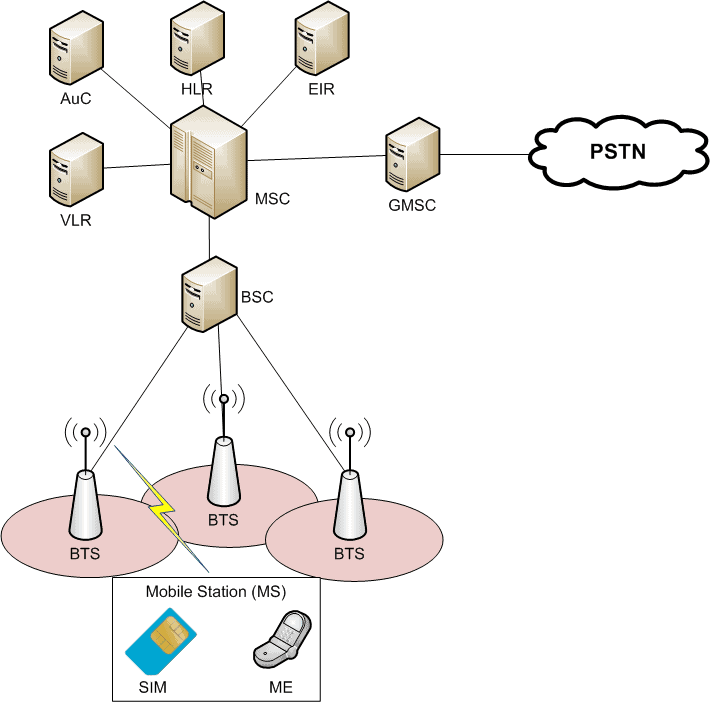
The GSM network consists of several key components that work together to facilitate communication. These components include:
- Mobile Station (MS): This is the user's device, such as a mobile phone or tablet.
- Base Station Subsystem (BSS): This includes the base transceiver station (BTS) and the base station controller (BSC), responsible for connecting the mobile stations to the network.
- Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS): This manages the connections between mobile stations and other networks, including landline networks.
- Operation Support Subsystem (OSS): This ensures the network operates smoothly and efficiently.
How Does the GSM Network Work?
The GSM network operates by using a combination of radio frequencies and digital signal processing. When a user makes a call or sends a text message, their device communicates with the nearest base station. The base station then routes the communication through the network to reach its destination.
Key processes involved in the GSM network include:
- Call Setup: The network initiates a connection between the calling and receiving parties.
- Authentication: The network verifies that the user is authorized to access services.
- Data Transfer: The actual voice or data is transmitted through the network.
- Call Termination: The connection is ended once the call is complete.
What Are the Benefits of Using a GSM Network?
Utilizing a GSM network comes with numerous advantages, such as:
- Global Coverage: The GSM network is available in most countries, allowing for international roaming.
- Interoperability: Different devices and networks can communicate seamlessly.
- Enhanced Security: GSM networks employ encryption to secure communications.
- Support for Multiple Services: Voice, SMS, and mobile data can all be managed within the same network.
What Are the Limitations of the GSM Network?
Despite its many benefits, the GSM network also has some limitations. These include:
- Limited Data Speeds: While 2G and 3G provided significant improvements, they still lag behind newer technologies like 4G and 5G.
- Dependence on Coverage: Users may experience connectivity issues in rural areas where network infrastructure is less developed.
- Compatibility Issues: Some advanced features may not be available on older GSM devices.
How Has the GSM Network Evolved Over Time?
The GSM network has undergone significant changes since its inception. Here’s a brief timeline of its evolution:
- 1980s: Development of GSM technology began in Europe.
- 1991: The first GSM network was launched in Finland.
- 2000s: The introduction of 3G technology significantly improved data speeds and services.
- 2010s: The rollout of 4G LTE began, further enhancing mobile internet capabilities.
What is the Future of the GSM Network?
The future of the GSM network is poised for further transformation, especially with the ongoing development of 5G technology. While 5G networks are set to provide faster speeds and lower latency, the GSM network will continue to play a critical role in connecting millions of users worldwide. It's likely that GSM technology will coexist with newer networks, ensuring that mobile communication remains accessible to all.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of the GSM Network
In summary, the GSM network is a fundamental component of modern telecommunications that has dramatically shaped the way we communicate. From its robust structure to its global reach, it remains an essential part of our everyday lives. As technology continues to advance, understanding the GSM network's principles will help users navigate the future of mobile communication effectively.
Love And Stardom: The Fascinating Journey Of The Can Yaman Couple
Creative And Fun Names For Turtles
Discovering The Life And Achievements Of Lilian De Vasconcelos Souza