The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) has revolutionized the way we connect and communicate, becoming a cornerstone of modern mobile networks. Its architecture, a complex yet efficient framework, plays a crucial role in facilitating seamless mobile communication across the globe. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of GSM network architecture, exploring its various components, functionalities, and significance in the realm of telecommunications. As mobile technology continues to evolve, understanding the foundational elements of GSM becomes increasingly important for both industry professionals and everyday users.
GSM network architecture is built on a layered framework that supports voice and data services, ensuring reliable connectivity for millions of users worldwide. From the core network to the radio access network, the architecture is designed to manage communication efficiently, addressing the growing demands of mobile users. This article aims to demystify the components of GSM network architecture, shedding light on how they work together to deliver exceptional service.
As we navigate through the components and functionalities of GSM network architecture, we will answer some key questions: What are the main elements of the GSM architecture? How do these components interact with each other? What role does the Mobile Switching Center play? By the end of this article, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of GSM network architecture and its significance in today's mobile communication landscape.
What Are the Main Components of GSM Network Architecture?
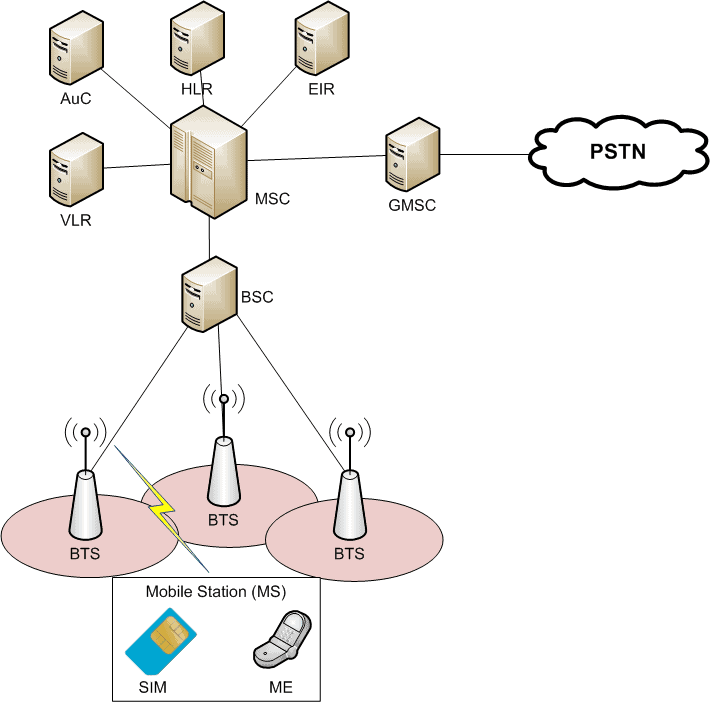
The GSM network architecture consists of several key components that work in conjunction to provide mobile communication services. These components include:
- Mobile Station (MS): The user's mobile device, which enables communication.
- Base Station Subsystem (BSS): This includes the Base Transceiver Station (BTS) and Base Station Controller (BSC) responsible for radio communication with mobile devices.
- Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS): This includes the Mobile Switching Center (MSC), which manages call routing and mobility.
- Operation Support System (OSS): This component manages network operation and maintenance.
How Does the GSM Network Architecture Function?
The GSM network architecture is designed to support various functionalities, including call setup, handover, and mobile management. Here’s a breakdown of how the architecture functions:
- Call Setup: When a call is initiated, the Mobile Station communicates with the BSS, which then connects to the NSS for call routing.
- Handover: If a user moves between coverage areas, the MSC ensures a seamless transition to maintain the call.
- Mobile Management: The system continuously tracks the location and status of mobile devices to facilitate communication.
What Role Does the Mobile Switching Center Play in GSM Network Architecture?
The Mobile Switching Center (MSC) is a pivotal component of the GSM network architecture. It serves multiple functions, including:
- Routing calls between different Mobile Stations.
- Managing mobile device registration and location updates.
- Facilitating handovers during ongoing calls.
What Are the Benefits of GSM Network Architecture?
The GSM network architecture offers several advantages that have contributed to its widespread adoption:
- Interoperability: GSM standards enable devices from different manufacturers to work together.
- Scalability: The architecture can easily accommodate a growing number of users and services.
- Cost-Effectiveness: GSM technology reduces operational costs for network providers.
How Has GSM Network Architecture Evolved Over Time?
Since its inception in the 1980s, GSM network architecture has undergone significant evolution to meet the demands of modern communication. Key advancements include:
- Introduction of GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) for data services.
- Implementation of EDGE (Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution) for improved data speeds.
- Transition towards 3G and 4G technologies, while maintaining GSM compatibility.
What Challenges Does GSM Network Architecture Face?
Despite its successes, GSM network architecture faces several challenges, including:
- Increased Data Demand: With the rise of smartphones and mobile applications, data traffic has surged.
- Security Concerns: Cybersecurity threats pose risks to user privacy and data integrity.
- Legacy System Limitations: Older GSM infrastructure may struggle to support newer technologies.
What Is the Future of GSM Network Architecture?
Looking ahead, the future of GSM network architecture appears promising. Key trends include:
- Integration with 5G technology for enhanced capabilities.
- Increased focus on IoT (Internet of Things) connectivity.
- Enhanced security measures to protect user data.
In conclusion, understanding GSM network architecture is essential for grasping the complexities of mobile communication today. Its foundational elements and evolving nature highlight its significance in a rapidly changing technological landscape. As we move forward, the continued development and adaptation of GSM architecture will play a crucial role in shaping the future of telecommunications.
Exploring The Wisdom Of Πόντι Λουσία Σοφία
Unveiling The Life Of Devayani's Husband: A Journey Of Love And Partnership
Embracing The Midweek Vibe: Inspiring Wednesday Quotes